|
Political Polarization in Jordan after the War on Gaza
Sahm Tell
Political polarization is not a new phenomenon in the Middle East, but in Jordan, the landscape has grown increasingly fragmented in recent years. The war on Palestine, particularly the recurrent hostilities in Gaza and the West Bank after October 7th, has profoundly influenced Jordan’s domestic politics and sociological tapestry, exacerbating existing divisions and creating deeper fault lines.
Read More > The Lebanese Presidential Election: A Key to Avoid Israel-Hezbollah Escalation? Bertille Lietar
On October 8, when Hezbollah opened a front in the South of Lebanon to support Hamas against Israel, it plunged the politically paralyzed country into an unpredictable dynamic, pushing the issue of the presidential vacuum into the background. Left without a President since October 2022 and without a fully-fledged Government or Parliament, the Lebanese state finds itself limited in controlling the extent of a conflict it is unwilling to entertain.
Read More > |
|
Russia and the Middle East: Discussions in Valdai
Yeghia Tashjian
On February 13-14, 2024, I received an invitation to attend the 13th Middle East Conference of the Valdai Discussion Club and the Institute of Oriental Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. The conference, titled “Time for Decisive Action: A Comprehensive Settlement for the Sake of Stability in the Region,” assembled more than 50 participants from 16 countries, mainly from Russia, Turkey, Iran, and Arab countries.
Read More > |
|
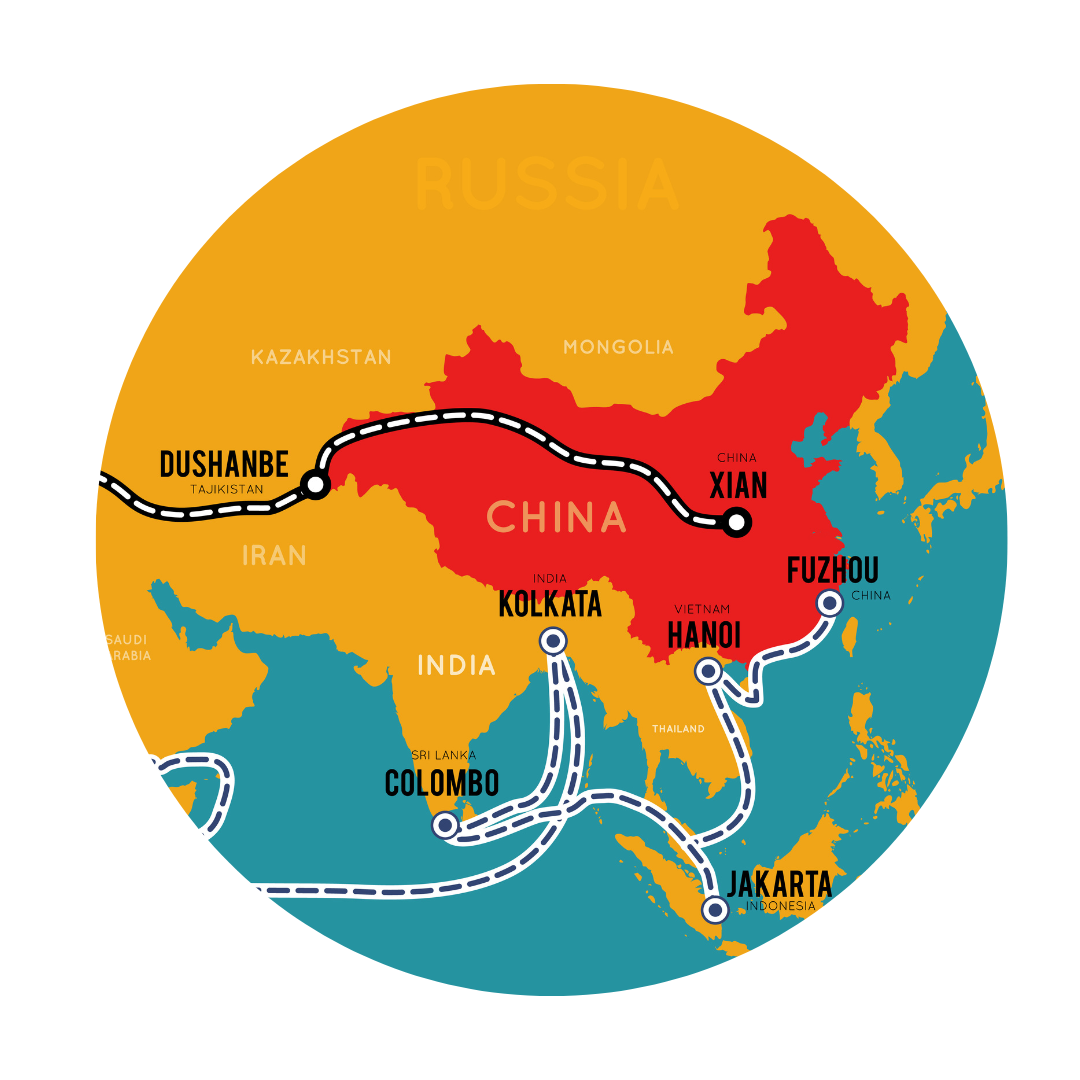
Bridging Horizons: Chinese Investments Reshaping MENA's Future
Nizar Bou Karroum
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), launched in 2013, has significantly expanded China's economic and political influence in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. The initiative, which consists of a new Silk Road Economic Belt and a maritime road, has drawn in 147 countries by 2023, primarily low and middle-income countries.
Read More > |
|
COP 28 Sees Compromises on Loss and Damage Demands in the Absence of Accountability for Big Polluters
Rami Abi Ammar
Established at last year’s COP27, the loss and damage fund became a central item on the agenda for negotiations at this year's United Nations Climate Conference, COP28, held in Dubai. The fund has been a tabled demand since 1991, as developing countries bearing the climatic brunt of historical emissions and continuing extraction activities by developed industrialized states seek finance for averting, minimizing, and addressing climate disasters.
Read More > |
|
COP 28: An Opportunity to Address the Vicious Cycle of Food Insecurity and Climate Change in the MENA Region
Mira Machmouchi
Food security has become an issue of international concern due to the ongoing geopolitical turmoil and magnifying impacts of a changing climate. Since 2011, food subsidies in the face of food insecurity in the MENA region cost up to $21.6 billion and were the highest in Iraq, Syria, and Egypt amounting to over 2% of their GDP.
Read More > |
The UAE is Walking a Fine Line in the Gaza WarJoe Boueiz
On September 15, 2020, at an official ceremony hosted by President Donald Trump at the White House, the Abraham Accords were signed by Israeli Prime Minister Benyamin Netanyahu and the foreign ministers of the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain, Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed Al Nahyan and Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani respectively. In the three years since the accords were signed, Israel and the UAE have deepened their ties in several areas such as trade, defense, technology, and energy. However, the outbreak of the conflict in the Gaza Strip, has put the UAE, and other signatories to the Abraham Accords, in an uncomfortable position. How will the UAE balance its profitable relationship with Israel amid the recent developments in Gaza?
Read More > |
The Opening of a Second Front in Lebanon Seems UnlikelyJoseph Bahout
The sudden, surprising and deadly attack launched by Hamas outside Gaza on the night of Oct. 7-8 may have shifted the Middle East as a whole into a dynamic that, in many respects, seemed to be moving away from lately. For more than two years, the region had been oscillating between tensions — some of them old, others new or renewed — and rapprochements — most of them transactional and cynical, but with a clear trend towards de-escalation, from Syria to Yemen, via the Iranian-Saudi detente.
Read More > |
What does the Expansion of the BRICS mean for the Middle East? Yeghia Tashjian
This year’s BRICS summit in South Africa came amid a tumultuous, almost entropic period in global politics. Intensifying U.S.-Chinese competition and the war in Ukraine have emphasized geopolitical trendlines. Meanwhile, many newly formed “medium-powers” frustrated by U.S. global politics have found ways to raise their concerns and challenge the unipolar system by reducing their dependency on the U.S. Dollar, while increasing bilateral trade in their own currencies.
Read More > |
Is the BRICS meeting in South Africa a big deal?Ishac Diwan
For their 15th annual meeting in South Africa, the main agenda item for the BRICS is their enlargement to new entrants – they now include five countries – Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. A popular joke goes by “nice bricks, but where is the mortar?” Perhaps that by growing, the group can get itself a better-defined agenda – in addition to a new name to replace an acronym put together by a British economist working at an American bank.
Read More > |
Voices from the Saint Petersburg International Economic Forum 2023Yeghia Tashjian
Between June 14-17, 2023 I had the opportunity to participate in a program organized by the “Friends for Leadership” to attend the Saint Petersburg International Economic Forum. Thousands of delegates mostly from Latin America, Africa, and Asia attended the forum alongside heads of state, diplomats, and businessmen. Interestingly, the UAE had the “special guest” status and anyone could feel its cultural, economic, and political presence in the forum. Delegates were anxious to be informed of the details of the new agreements signed between Russia and other countries, Russia’s President Vladimir Putin’s remarks and attend dozens of sessions and panels related to the BRICS, Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), International North-South Transport Corridor, and North-South trade. Personally, I had the opportunity to closely identify Russia’s post-Ukraine war foreign policy priorities, its geo-economic interests in the Middle East, and the challenges of the emerging multipolar world system.
Read More > |
Can social activism for a new economic model get us out of our deep hole?Ishac Diwan
Lebanon is in a deep hole. Not only is its financial sector badly broken, but so is the state and indeed, its economic model. The country is now much poorer and more unequal. We are stuck in a poverty trap, and it will take generations, or a miracle, before the proverbial phoenix manages yet another rebirth.
This piece, like many written these days, is a search for how to shorten the time to resurrection. There is no easy answer. I will dare to argue that if there is a miracle, it would have to be an economic one. That it can only be engineered by civil society and citizens associations. And that it is unlikely to be of the sudden salvation type, but rather, that it would require several years of activism and organizational work to start showing progress. In the process, I will indulge in multiplying references to my recent work on related issues. Read More > |
Cholera Outbreak and WEF Nexus Frameworks in LebanonGhida Soubra
As Lebanon struggles amid poor sanitation and collapsing infrastructure exacerbated by the unprecedented and ongoing economic crisis, October 2022 marked the first cholera outbreak in almost three decades. The near epidemic currently being witnessed illustrates the utmost need for adopting a Water-Energy-Food (WEF) nexus approach. The WEF nexus reflects a holistic, socio-ecological system perspective that values all three sectors equally and draws on the synergies among them.
Read More > |
|
|
Cholera in Lebanon: Challenges and Opportunities within the Water SectorRami Abi Ammar
Cholera is an acute diarrheal disease arising from the ingestion of the Vibrio cholerae bacterium through fecally-contaminated water or food. People infected with cholera may lose up to 25 liters of fluid per day due to vomiting and diarrhea. The loss of fluid and salts can cause severe dehydration and death within hours if patients are not treated promptly and adequately. Cholera outbreaks are often linked to poor water and sanitation infrastructure that facilitates the spread of the bacterium within water and food systems. As such, the risk of cholera epidemics is higher in humanitarian emergency settings, including settlements and crowded areas of displaced populations that lack adequate access to clean water, sanitation and health services. The incubation period of the Cholera bacterium is relatively short (between two hours and five days); therefore, the number of cases and fatalities can increase rapidly, creating serious public health concern.
Read More > |
Latest on IFI's Blog
|
مُقاربة لتحرير أسعار الطاقة في ظلّ الأزمات المُتعدّدة في لبنان
Read More > Navigating Through Lebanon’s Looming Water Crisis
Read More > |
How Things Fall Apart
Read More> This time, Lebanon will not be saved by outsiders
Read More > |